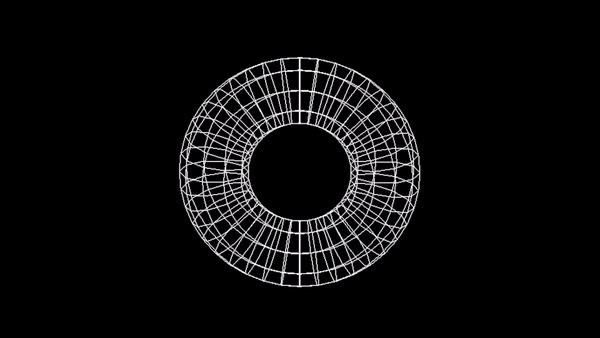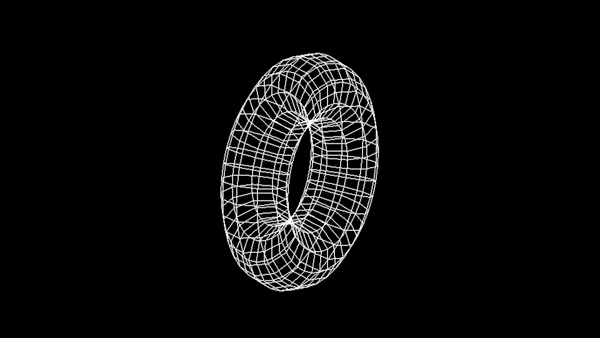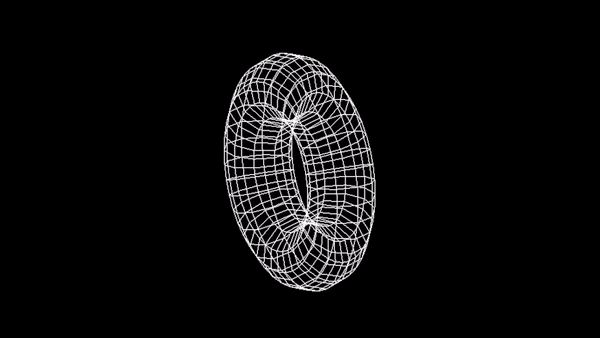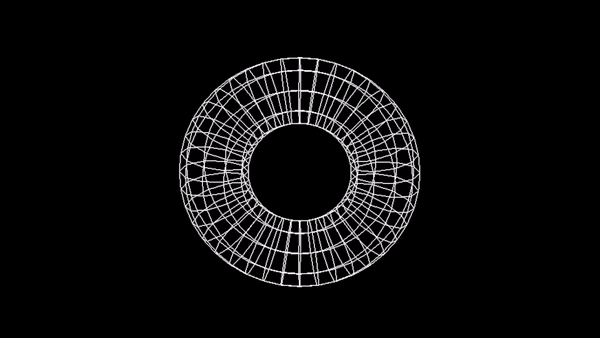
Model szkieletowy sześcianu:
#include <gl/glut.h>
#include <cmath>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
double eyex = 0.5;
double eyey = 1;
double eyez = 3;
struct Vec3 {
double x, y, z;
};
void cube()
{
vector<Vec3> v {
{-1,-1, 1}, // 0
{ 1,-1, 1}, // 1
{ 1, 1, 1}, // 2
{-1, 1, 1}, // 3
{-1,-1,-1}, // 4
{ 1,-1,-1}, // 5
{ 1, 1,-1}, // 6
{-1, 1,-1}, // 7
};
// 7 - 6
// / /|
// 3 - 2 5
// | |/
// 0 - 1
vector<vector<int>> f {
{0,1,2,3},
{5,4,7,6},
{0,3,7,4},
{1,5,6,2},
{3,2,6,7},
{1,0,4,5}
};
for(int i=0; i<(int)f.size(); ++i)
{
glBegin(GL_LINE_LOOP);
for(int j=0; j<(int)f[i].size(); ++j)
{
glVertex3d(v[f[i][j]].x, v[f[i][j]].y, v[f[i][j]].z);
}
glEnd();
}
}
void myDisplay() {
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW);
glLoadIdentity();
gluLookAt(eyex,eyey,eyez, 0,0,0, 0,1,0);
cube();
glFlush();
}
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
glutInit(&argc, argv);
glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_SINGLE|GLUT_RGB);
glutInitWindowSize(500, 500);
glutInitWindowPosition(0, 0);
glutCreateWindow("GLUT WINDOW");
// Orthographic projection
glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION);
glLoadIdentity();
glOrtho(-2,2,-2,2,0,100);
glutDisplayFunc(myDisplay);
glutMainLoop();
}Zadanie 1 - Animacja
Dodaj do powyższego programu animację poprzez zmianę (eyex, eyey, eyez)
Zadanie 2 - Wireframe Sphere
Utwórz animację sfery na wzór:
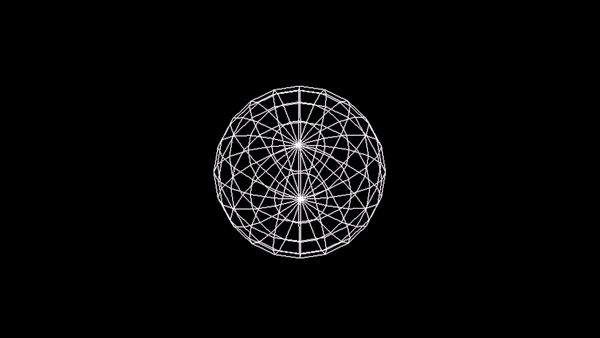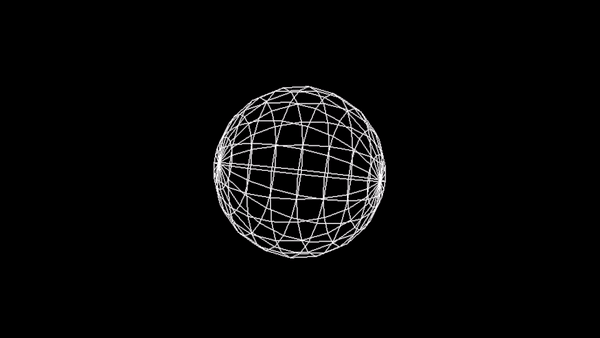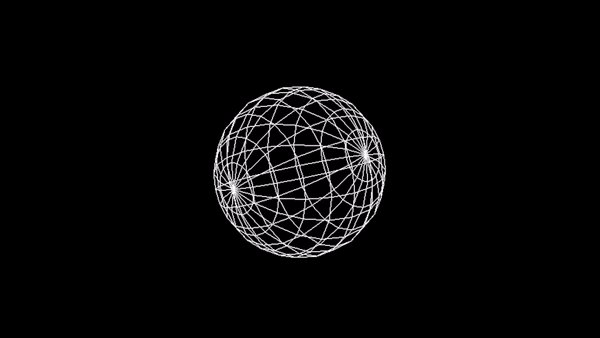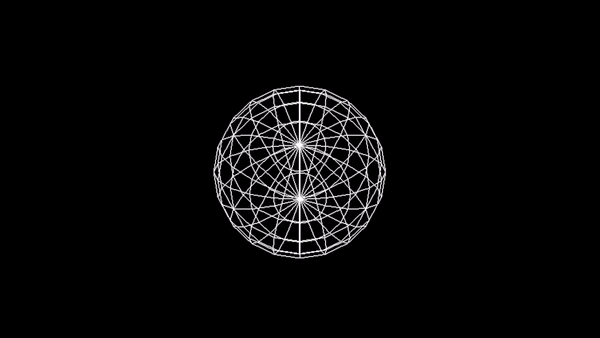
Zadanie 3 - Wireframe Torus
Utwórz animację torusa na wzór: